이 컨텐츠는 시리즈물입니다.
[proxy 1편] Proxy Pattern(프록시 패턴)이란?(feat. Java): https://joosjuliet.github.io/proxy_pattern/
[proxy 2편] Dynamic Proxy란?(feat. Spring):
https://joosjuliet.github.io/dynamic_proxy/ [proxy 3편] Dynamic Proxy와 트랜잭션?(feat. Spring): https://joosjuliet.github.io/transaction/
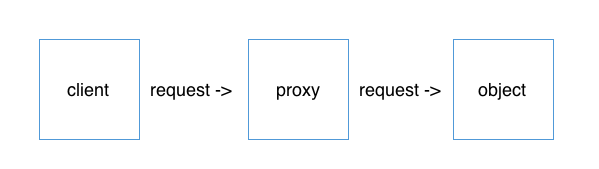
Proxy 패턴
실제로 액션을 취하는 객체를 대신해서 “대리자 역할”을 해 자신이 보호하고 있는 객체에 대한 액세스 권한을 제어하는 전략
Proxy이 나온 배경과 설명
객체에 관한 권한을 부여를 직접 했으면 좋겠고, “필요에 따라” 객체를 생성시키거나 사용해 메모리를 절약하고 싶어서 만든 것이다.
Proxy로 만드는 핵심 방법
interface와 interface를 상속받은 class를 만든다.
- interface를 implements한 class에 높은 cost(네트워크 연결, 메모리 안의 커다란 객체, 파일, 또 복제할 수 없거나 수요가 많은 리소스)를 하는 method가 있으면 메모리 낭비가 심하다.
- 그래서 일단 똑같은 interface를 상속받는 class들을 만들고, 그중 한 class를 높은 cost를 가지고 있는 method를 갖게 한다.
- 나머지 class는 그 class를 인스턴스화 해서 그 높은 cost를 가진 메소드에 접근을 결정한다.
Proxy 구현방법
- 일단 CommandExcutorImpl, CommandExecutorProxy는 똑같은 인터페이스(CommandExecutor)를 상속받음으로 인터페이스의 일관성을 유지한다.
- 생성자에서 CommandExcutorImpl 클래스를 인스턴화 시키고, 인스턴스화 된 executor 객체의 runCommand 메소드를 프록시 클래스의 runCommand 메소드에서 액세스를 결정한다.
public interface CommandExecutor {
public void runCommand(String cmd) throws Exception ;
}
public class CommandExcutorImpl implements CommandExecutor {
@Override
public void runCommand(String cmd) throws IOException {
// 높은 cost를 가진 method
Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd);
System.out.println("cmd: " + cmd);
}
}
public class CommandExecutorProxy implements CommandExcutor {
private boolean isAdmin;
private CommandExecutor executor;
public CommandExecutorProxy(String user, String pwd) {
if ( "seotory".equals(user) && "pw".equels(pwd) ) {
isAdmin = true;
}
executor = new CommandExcutorImpl();
// 생성자에서 CommandExcutorImpl 클래스를 인스턴화
}
@Override
public void runCommand(String cmd) throws Exception {
// 생성자에서 만든 인스턴스화 된 executor의 runCommand 메소드를 액세스 할지 말지를 결정한다.
if (isAdmin) {
executor.runCommand(cmd);
} else {
if (cmd.trim().startsWith("rm")) {
throw new Exception("rm is only admin");
} else {
executor.runCommand(cmd);
}
}
}
}
@testing
public class ProxyPatternTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CommandExcutor executor = new CommandExecutorProxy("seotory", "is_not_pw");
try {
executor.runCommand("ls -al");
executor.runCommand("rm -rf *"); // proxy 클래스에 의해 에러가 날 것이다. -> 위에서 pw가 아닌 is_not_pw로 썼기에
} catch (e) {
System.out.println("Exception Message: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
결과 output
cmd: ls -al
cmd: rm -rf *// proxy 클래스에 의해 에러가 날 것이다. -> 즉 권한 관련 일 CommandExecutorProxy이 한다.
Exception Message: rm is only admin
적용 포인트
-
프록시 패턴의 잘 알려진 예로는 참조 횟수 스마트 포인터 객체이다.
- 가상 프록시
- 높은 cost 객체 대신 스켈레톤 객체(인터페이스만 존재하고 실제로 인스턴스를 생성하지 않는 객체)를 사용하여 실질적으로 객체가 필요할때까지 높은 cost의 객체 생성을 지연시켜 메모리를 절약할 수 있다.
- 원격 프록시
- 서로 다른 머신에 있는 객체에 대해 제공할 수 있다(또는 객체를 사용할 수 있다). 일반적인 예는 JAVA의 RMI(다른컴퓨터에서 함수가져오는 것)이다.
- 보호 프록시
- 객체에 대해 액세스 할 수있는 권한을 부여할 수 있다.
- 정교한 참조
- 프록시 객체에 정교한 작업을 부여할 수 있다. 예를들어 객체를 생성할 때 카운팅 기능을 추가적으로 작업할 수 있다.
참고: 메소드 사진 참고:
http://ehpub.co.kr/tag/%ED%94%8C%EB%9D%BC%EC%9D%B4%EA%B8%89-%ED%8C%A8%ED%84%B4-flyweight-pattern/
프록시패턴 참고 : https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/%ED%94%84%EB%A1%9D%EC%8B%9C_%ED%8C%A8%ED%84%B4
https://blog.seotory.com/post/2017/09/java-proxy-pattern
aop에서 사용하는 다이나믹 프록시:
https://haviyj.tistory.com/28 [Duck Programming]
출처: https://haviyj.tistory.com/26?category=695904 [Duck Programming] 출처: https://haviyj.tistory.com/28 [Duck Programming]